Breast Reconstruction
Can a nipple be reconstructed?
Some types of mastectomy leave the nipple and areola in place (nipple-sparing mastectomy). The areola is the dark skin surrounding the nipple. If necessary, providers can create a new nipple. They do this by transferring skin from another part of your body (skin graft) or local skin on the breast to shape into a nipple.
Some people choose to get a 3D tattoo of an areola after nipple reconstruction. Specially trained tattoo artists create realistic images of an areola.
How do I know what type of breast reconstruction surgery to get?
Your provider will recommend the most appropriate technique for you based on:
Your age, overall health and lifestyle.
The kind of mastectomy or lumpectomy you had and how much tissue remains.
Whether you need additional treatments for breast cancer (such as chemotherapy or radiation).
Past surgeries you’ve had that may make it difficult or impossible to take a flap from your belly. One example is abdominal surgery.
Your goals and desired appearance.
What does breast reconstruction treat?
Most often, breast reconstruction happens after surgery to treat or prevent breast cancer. Providers use it to reshape breasts and rebuild damaged or missing tissue. They may also perform this surgery to restore symmetry. This means they make both breasts the same size and shape. Less commonly, providers reconstruct breast tissue that results from congenital abnormalities (birth defects).
After a mastectomy, it’s normal to mourn the loss of your breast. Breast reconstruction surgery helps many people manage these strong emotions and move forward.
What happens before breast reconstruction surgery?
Breast reconstruction happens after a mastectomy or lumpectomy. If you have breast cancer, you may also need chemotherapy or radiation before breast reconstruction surgery. Your surgeon will ask you about your goals and discuss your surgical options with you.
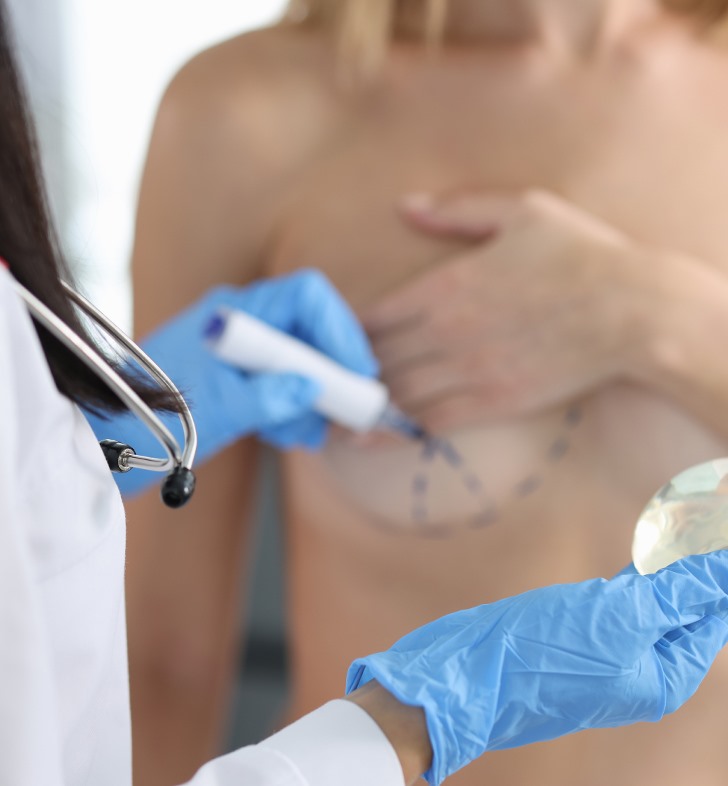
First, your surgeon will conduct a comprehensive examination. They will measure and take photographs of your breasts. Tell your provider about your health, medications you take and any surgeries you’ve had. Your provider may ask you to stop taking certain medications before the procedure.
What happens during breast reconstruction surgery?
A surgeon will perform your breast reconstruction surgery in a hospital. Your provider gives you anesthesia, so you’ll be asleep and you won’t feel any pain during the surgery. If you’re having a mastectomy or lumpectomy, your surgeon will do that procedure first.
While you’re still asleep, your surgeon performs the breast reconstruction. If you’re getting implant reconstruction, they place the implant in your chest. If you're having a flap procedure, they take tissue from one part of your body, form and place the new breast.
During surgery, your provider may insert a drain (a thin tube) under your skin. One end of the tube sticks out from your chest. The tube drains fluid and blood as you recover. Your provider will remove the tubes when you don’t need them anymore.
What happens after breast reconstruction surgery?
After surgery, you may need to stay in the hospital for up to a week. Your team of providers will watch you to ensure you’re healing. You may wear a surgical bra. As your breasts heal, the bra supports your breasts and reduces swelling. When it’s time to go home, your provider will give you instructions detailing how to care for yourself.
Your provider will help you manage pain after surgery. They may recommend prescription or over-the-counter pain medication. Follow your provider’s instructions carefully when taking medication.
If you had reconstruction on one breast, you may need more surgery to make your breasts match. This may include breast reduction surgery or breast augmentation.
What are the advantages of breast reconstruction surgery?
Breast reconstruction surgery can improve self-confidence after a mastectomy or lumpectomy. After breast reconstruction, many people feel better about how their clothes fit. They may also feel more comfortable wearing a swimsuit.
Many people choose not to have breast reconstruction after a mastectomy. Instead, they wear a breast form (prosthesis) inside a special bra. They may also choose to “go flat” and not wear prosthetic breasts. The decision is very personal and varies from person to person.
What are the risks or complications of breast reconstruction surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, risks of breast reconstruction include infection and bleeding. Results vary depending on the type of procedure and how much tissue remained after breast cancer surgery and radiation.
After surgery, you’ll probably have little or no sensation in your newly reconstructed breasts. Over time, you may regain some sensation in the skin. But it won’t feel like it did before.
Complications of breast reconstruction surgery may include:
Blood clots. These may be more likely to happen after some types of flap reconstruction surgeries.
Breasts that are a different size or shape. One may feel more firm than the other. The nipples and areolas may not be symmetrical.
Bruising or scarring around the reconstructed breasts. All breast reconstruction surgeries leave scars. They may fade over time.
Fat necrosis. Death of the transplanted tissue after flap surgery.
Problems with the implants (for implant reconstruction). These problems can include wrinkling, rippling and ruptures (tears) in the implant.
Weakness, pain or sensitivity at the donor site after a flap reconstruction procedure. Donor sites may include the lower belly, thigh, back or bottom.